Fast food: Convenient, yet harmful – why?
Interesting
−
15 April 2025 6813 3 minutes
Fast food has become one of the most in-demand products of modern life. Today, such food outlets can be found in nearly every corner of the city. In addition to its appealing taste, the widespread availability of door-to-door delivery services continues to attract consumers. For many, the only barrier seems to be affordability. However, beyond its impact on the wallet, fast food also weighs heavily on one’s health. While its disadvantages have long been discussed, this article also touches on the lesser-known benefits of fast food.
What are the advantages of fast food?

Indeed, while some fast food items can be costly, many remain affordable and convenient—especially for those on the go. Despite its frequent criticism, fast food does offer certain advantages, including:
- Delicious and flavorful options
- Quick and efficient delivery services
- Eliminates the daily question of “what to cook?”
- Easily accessible—fast food cafes are available at almost every turn
- Convenient for multitasking while eating
- Packaged for travel and portability
What makes fast food harmful?

Despite its taste and convenience, the harmful effects of fast food are significant and well-documented. While it helps save time and energy, the health consequences can be serious. From heart disease to obesity, here are the key risks associated with fast food consumption:
Cardiovascular disease
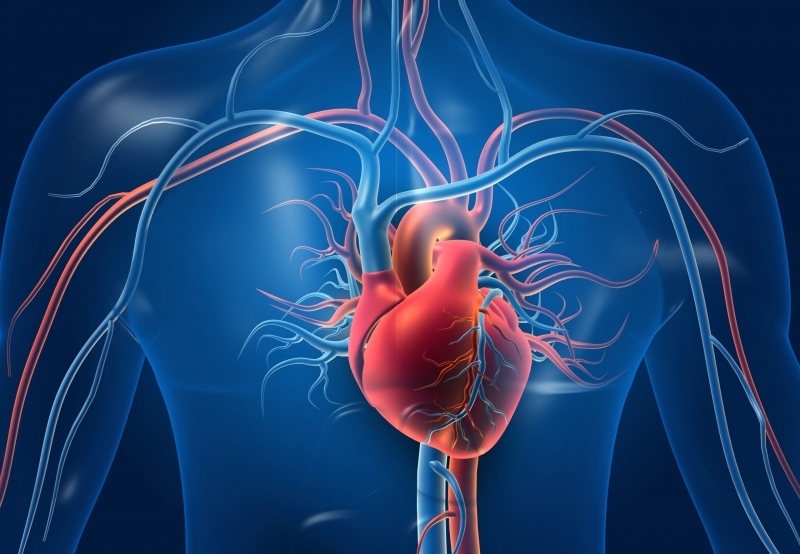
Fast food is often categorized as “junk food” due to its high levels of saturated fats, which raise bad cholesterol and strain the heart. In addition, the excessive sodium content can lead to high blood pressure. Long-term consumption of such food can increase the risk of heart disease.
Hygiene concerns

Hygiene in the fast food industry is often questionable. While speed is a priority for many chains, proper sanitation is not always guaranteed. Some establishments may prioritize quantity over quality, and the conditions behind the counter are not always visible to customers.
Weight gain and obesity
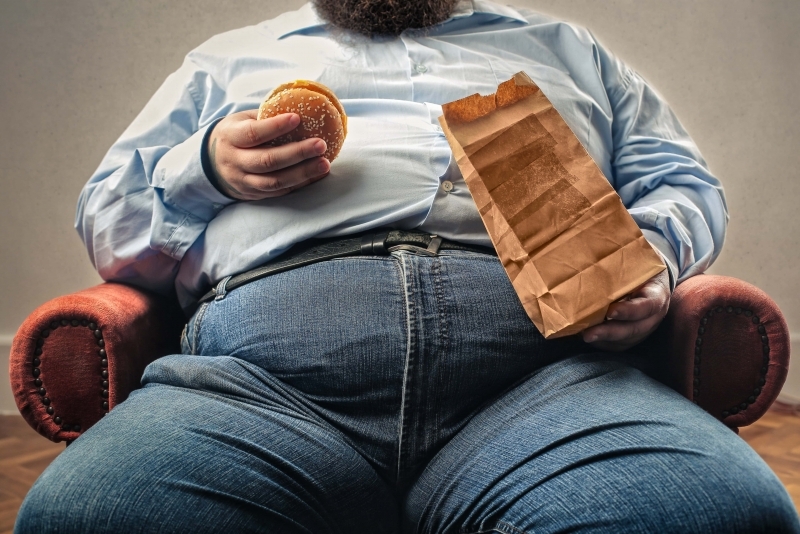

Frequent consumption of calorie-rich, fatty fast food—often paired with sugary, carbonated beverages—can lead to excessive weight gain. These high-glucose combinations contribute significantly to the obesity epidemic.
Low nutritional value
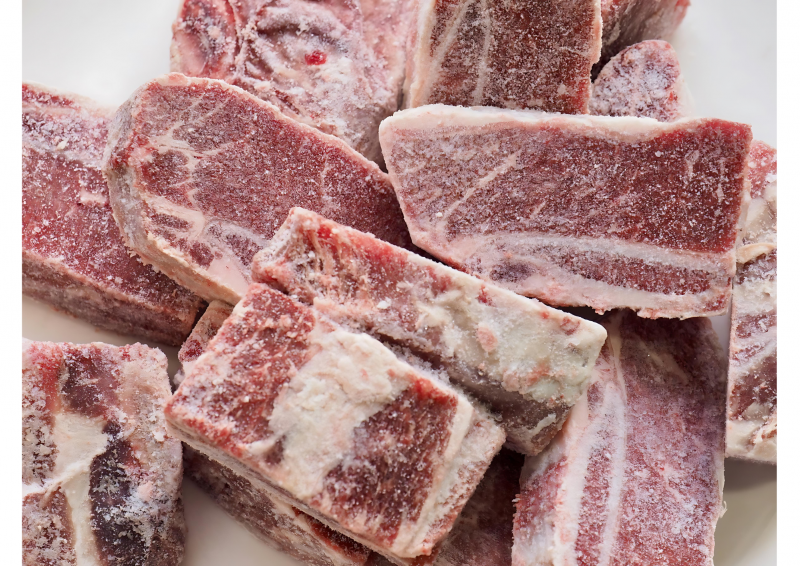

Many fast food items are made using frozen and pre-processed ingredients, which lose nutritional quality the longer they are stored. To ensure speed and efficiency, many chains compromise on fresh, nutrient-rich products, leaving the body deprived of essential vitamins and minerals.
Digestive issues
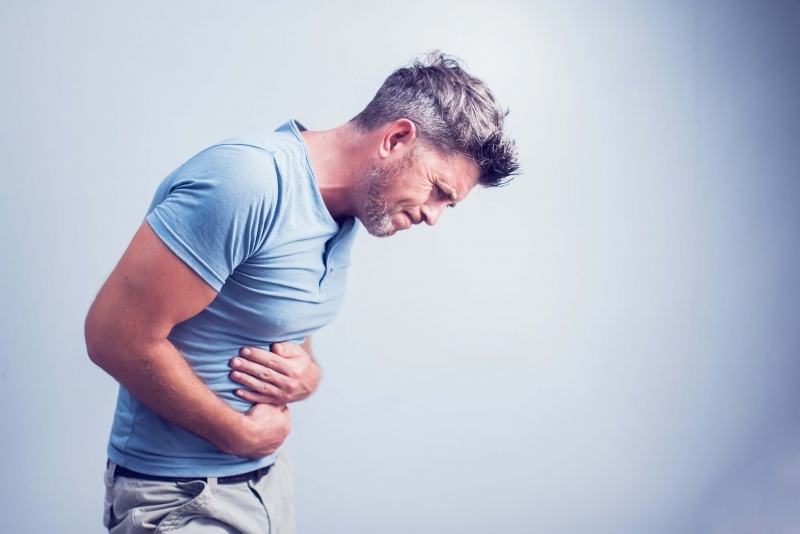

Fast food often contains artificial additives, spices, and heavily processed components used to enhance flavor. These can disrupt the digestive system, leading to conditions such as bloating, constipation, stomach ulcers, and even increased risk of carcinogenic exposure.
Obesity risk
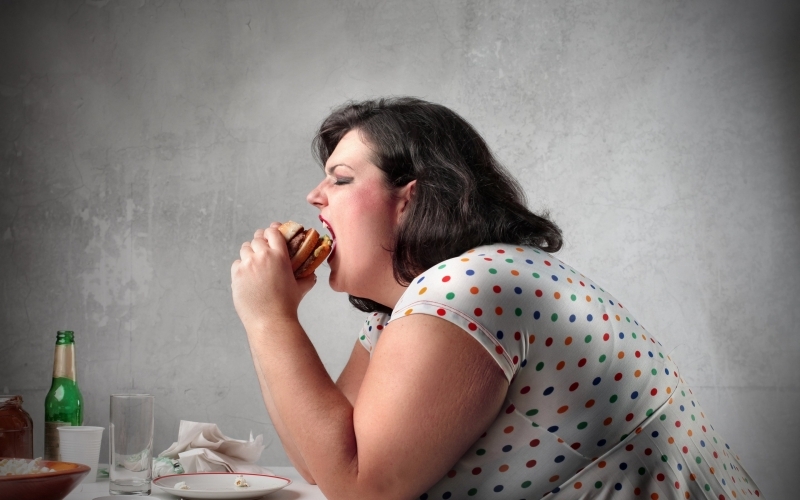

Regular consumption of fast food high in carbohydrates and saturated fats leads to fat accumulation in the body. Over time, this results in obesity, a major public health concern globally.
Kidney and liver strain
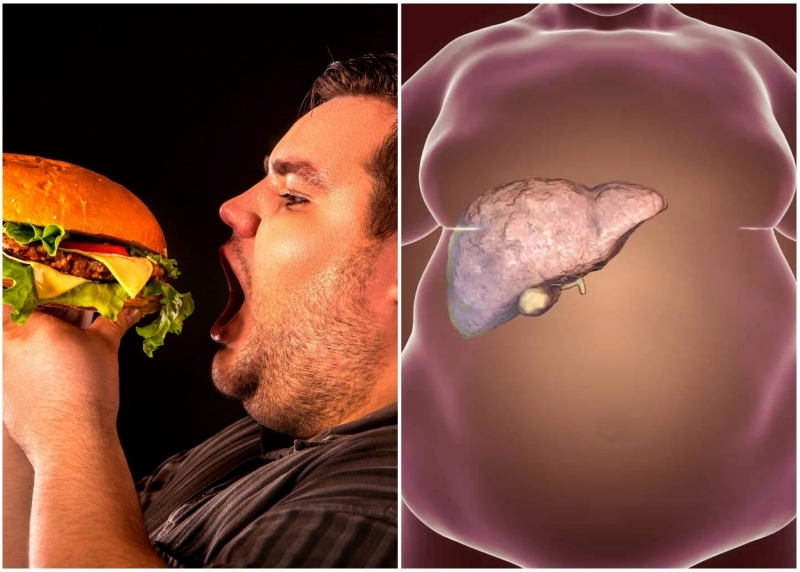
Fried foods like French fries and burgers contain processed salts that negatively affect kidney and liver functions. These salts alter enzyme activity and disrupt the liver’s balance, while trans fats accumulate in liver tissue. High sodium intake also contributes to elevated blood pressure and impaired kidney performance.
It is important to note that most fast food is either undercooked or deep-fried in reused oils. Additionally, artificial additives are often used to enhance taste, further compounding health risks.
Ultimately, the human body reflects what it consumes—whether food is prepared slowly or quickly. The long-term effects will eventually become apparent. The choice, however, remains in each individual’s hands.




